scour test for labral tear|Hip Labral Disorders : Chinese The Scour test, sometimes called the quadrant test, is a technique used to evaluate the joint as a cause of hip pain. The patient is supine. The examiner flexes the hip and knee to approximately 90 degrees. A variety of research looks at the sterilizing effects of autoclaves on the physical qualities of NiTi endodontic files, with varying results.
{plog:ftitle_list}
This guide will briefly explain the most common issues across manufacturers, to help you get back to your work. Exercise particular care when working with any electrical and/or pressurized device. Always defer to your .
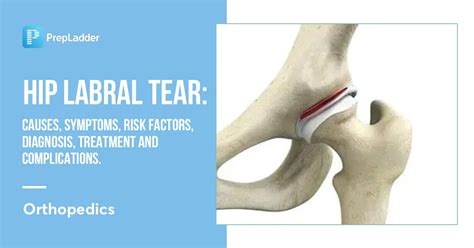
A positive hip quadrant test is indicative of an osteochondral lesion, early to late-stage osteoarthritis, capsular tightness or joint hypomobility, avascular necrosis, or even an acetabular labral tear, depending on the proximity of the tear to the compressed joint surfaces.

alpco elisa kit
The Scour test, sometimes called the quadrant test, is a technique used to evaluate the joint as a cause of hip pain. The patient is supine. The examiner flexes the hip and knee to approximately 90 degrees.This test works by scouring the femoral acetabular joint for pathology. The compression of the femur, through the various ranges, stresses the bone, labrum, cartilage, ligaments, etc. While this test has been labeled as the "hip clearing test," due to the low diagnostic accuracy, it should not necessarily be used as such.October 10, 2018. Objectives. Describe anatomical and physiological characteristics of the acetabular labrum predisposing it to injury. Outline risk factors contributing to the development of acetabular labral tears. Identify common biomechanical/musculoskeletal deficiencies in patients with acetabular labral tears.
Special Tests for the Hip Exam
Peer-Reviewed. Diagnosing labral tears in the hip involves: Evaluating the hip joint to check for labral problems. Conducting specific hip labral tear tests to determine if the labrum may be torn or degenerated. Identifying or ruling out other hip conditions contributing to the patient’s symptoms.The scour test can be used to evaluate for hip arthritis and labral tears. The examiner flexes the patient's hip and knee. They passively move the patient th.
Special testing is generally performed following a full examination of the shoulder that includes but is not limited to patient history, mechanism of injury, clinical observation, bony and soft tissue palpation, assessment of active and passive physiological movements, assessment of passive arthokinematic / accessory joint mobility, neurological.Hip Scour Test. Tests for Hip labrum, capsulitis, osteochondral defects, acetabular defects, osteoarthritis, avascular necrosisand femoral acetabular impingment syndrome. The subject should be in supine with the examiner standing on the involved side. Tests: Thomas test, leg length measurement, resisted hip abduction, ligamentous stability, passive internal rotation of hip, passive hip adduction, Faber test, Scour test and resisted SLR, neural tension tests. 8 When positive, these last 3 tests indicate theLabral tears of the hip are a common cause of intra-articular hip pain in athletes. The labral stress test, also known as the scour maneuver, is performed with the patient supine starting with the affected hip in abduction and external rotation.
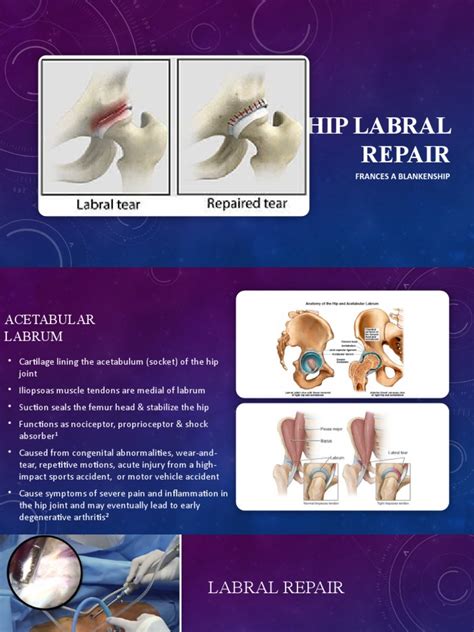
Hip Labral Disorders
Diagnosing a Hip Labral Tear
A positive hip quadrant test is indicative of an osteochondral lesion, early to late-stage osteoarthritis, capsular tightness or joint hypomobility, avascular necrosis, or even an acetabular labral tear, depending on the proximity of the tear to the compressed joint surfaces.
The Scour test, sometimes called the quadrant test, is a technique used to evaluate the joint as a cause of hip pain. The patient is supine. The examiner flexes the hip and knee to approximately 90 degrees.
This test works by scouring the femoral acetabular joint for pathology. The compression of the femur, through the various ranges, stresses the bone, labrum, cartilage, ligaments, etc. While this test has been labeled as the "hip clearing test," due to the low diagnostic accuracy, it should not necessarily be used as such.
October 10, 2018. Objectives. Describe anatomical and physiological characteristics of the acetabular labrum predisposing it to injury. Outline risk factors contributing to the development of acetabular labral tears. Identify common biomechanical/musculoskeletal deficiencies in patients with acetabular labral tears.Peer-Reviewed. Diagnosing labral tears in the hip involves: Evaluating the hip joint to check for labral problems. Conducting specific hip labral tear tests to determine if the labrum may be torn or degenerated. Identifying or ruling out other hip conditions contributing to the patient’s symptoms.The scour test can be used to evaluate for hip arthritis and labral tears. The examiner flexes the patient's hip and knee. They passively move the patient th.Special testing is generally performed following a full examination of the shoulder that includes but is not limited to patient history, mechanism of injury, clinical observation, bony and soft tissue palpation, assessment of active and passive physiological movements, assessment of passive arthokinematic / accessory joint mobility, neurological.
Hip Scour Test. Tests for Hip labrum, capsulitis, osteochondral defects, acetabular defects, osteoarthritis, avascular necrosisand femoral acetabular impingment syndrome. The subject should be in supine with the examiner standing on the involved side. Tests: Thomas test, leg length measurement, resisted hip abduction, ligamentous stability, passive internal rotation of hip, passive hip adduction, Faber test, Scour test and resisted SLR, neural tension tests. 8 When positive, these last 3 tests indicate the
Improved chemical and chromatographic methods for the isolation of electrophoretically pure K-casein have been developed. The chemical method is simple, mild, reproducible, and can be .
scour test for labral tear|Hip Labral Disorders